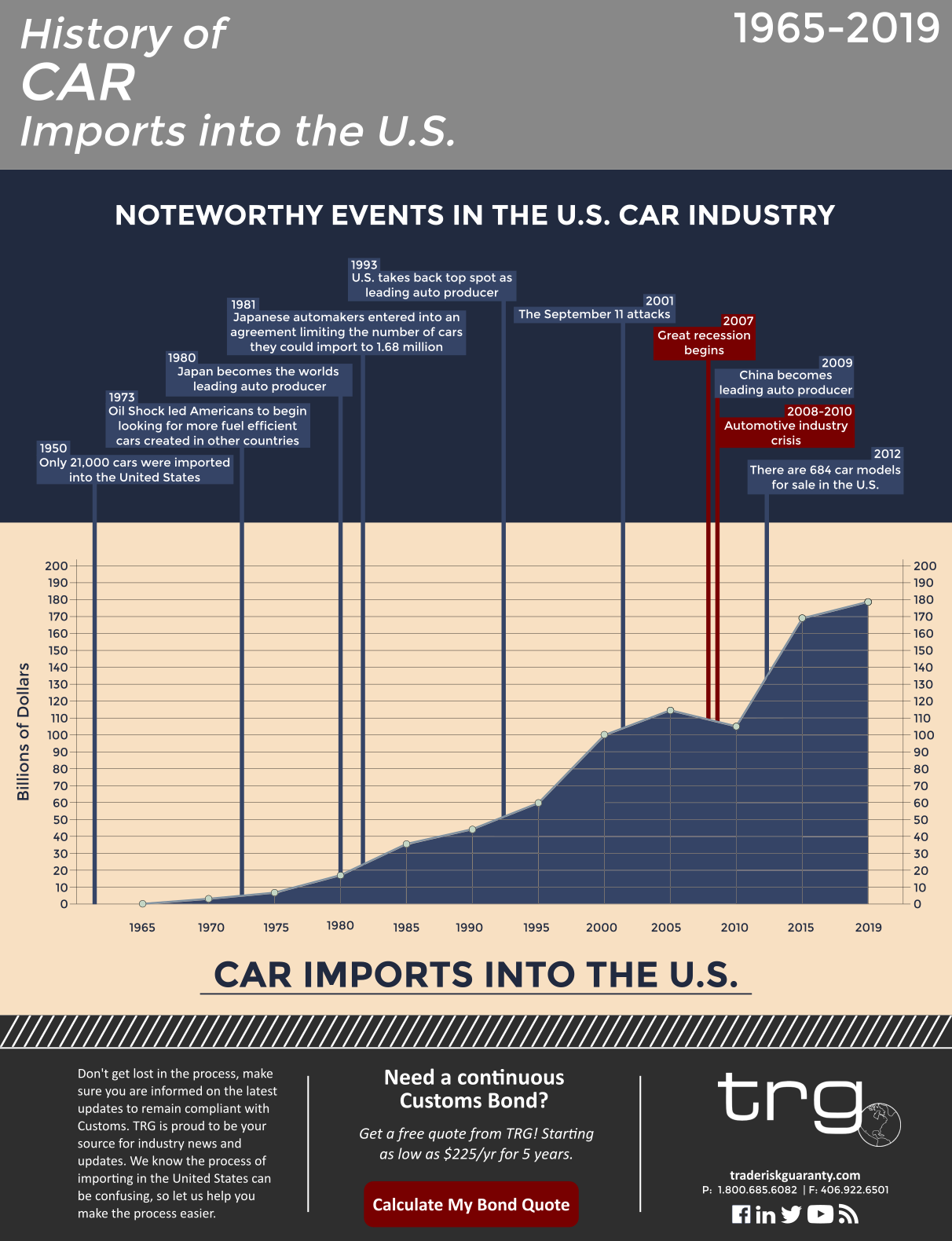
The number of United States car imports has exponentially increased since the late 1950’s when cars first came across the ocean to the U.S.
Americans love and need their motor vehicles. Since the initial mass production of the automobile, the United States auto industry has grown to be a vital part of the economy. Because of this, cars have become one of the most imported items into the United States.
The History of the Automobile Industry in the United States
An increase in spending on car imports is directly linked to the development of the auto manufacturing industry and to the U.S. economy. So if we compare the monetary amount spent on importing cars into the United States with a timeline of important developments in the auto industry, we can begin to see the correlation between the two.
Below details some of the important events that have had an effect on the number of United States car imports.
- The U.S. automobile industry exploded after the end of the Second World War in 1945. With the creation of the highway system and a boom in the economy, Americans had the funds and a reason to purchase automobiles. Car owners could now drive cross-country in their own personal vehicles.
- During the ’50s and ’60s the first cars were imported into the U.S. and by the ’70s Japanese technology was importing more fuel-efficient cars than Americans.
- In the 1970s and ’80s, the car imports slowly grew as the demand for cars increased. Companies such as Toyota engineered higher quality cars which could be sold at a low cost. These cars became more popular when the price of gas in the U.S. spiked in 1973 and 1980. Eventually, the foreign competition led American producers to catch up with technology to remain competitive with foreign producers.
- Spending on car imports grew consistently every year during the ’80s and ’90s. Quickly, the imported car industry captured a large market share in the U.S. and in 1980 Japan became the world’s leading auto producer, this spot would later be taken back by the U.S. in 1993 and then China in 2009. Throughout these years, the vehicles became necessary for business and pleasure.
- Imports of automobiles increased consistently for many years until a sharp drop in the mid to late 2000s. The U.S. automobile crisis happened in 2008 and the demand for cars dropped drastically, major auto companies posted massive losses. The three biggest auto manufacturers in the U.S. needed government assistance to stay in business. Additionally, manufacturers in Asia were forced to cut production due to falling demand. Toyota experienced its first loss in over 70 years of operation. As seen in the graphic below, the automotive crisis hit the industry hard during these years.
- Despite international events, car imports recovered and quickly bounced back after 2010. Presently American automobile companies have plants across the world, in the U.S. and other partnering countries.
- This past year, $179 Billion worth of cars were imported into the United States.
History and Data Comparison of United States Car Imports
From the graphic, you can see that United States car imports have steadily grown since the 1960s. The one notable dip (which is considerably large) reflects the auto crisis (2008-2010).
Click the image for a downloadable PDF
The Current Market for Cars Imported into the United States
Presently, automobiles make up 8.3% of total imports into the U.S. and are the most imported commodity. In 2018, $179 billion worth of cars were imported into the U.S., the majority of these vehicles coming from China, Mexico, Japan, Canada, and Germany.
Currently, the imported automobile industry faces some big decisions to be made within 180 days of May 17, 2019. President Trump has threatened to impose a 25% tariff on all automobile and automobile parts imported into the United States. An investigation is currently underway to determine the effect of foreign auto manufacturers on the U.S. This threatens to completely change the industry, new car prices would rise and the number of cars manufactured in the U.S. would increase with the implementation of a 25% tariff.
Stay up to date with the current trade war and subscribe to the Trade Risk Guaranty YouTube page.